Enhance your business analysis skills today! Explore the tools, techniques, and strategies needed to make projects successful. Read more now!
Join the Telegram Channel: Click Here!
Apply Link For Business Analyst Position: Click Here!
Top 10 To Crack Business Analyst Interview Questions.
What is called requirement analysis?
Requirements analysis is a critical base for any successful project. It involves proactively exposing and carefully describing the ‘essential needs and expectations’ of all stakeholders before embarking on the development journey.
During this phase, business analysts use interviews, workshops, and other investigative techniques to gather information from a variety of stakeholders. Stakeholders can include clients, end users, internal teams, and anyone else who will be affected by the project.
The goal is not only to understand the clearly stated needs but also to dig deeper to uncover any underlying pain points or unspoken desires.
Explain the SWOT analysis and how It’s relevant to business analysis.
SWOT analyses are categorized into strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Analysis is a key tool for business analysts, offering a comprehensive snapshot of a business’s internal and external landscape.
Analyzing internal factors:
- Strengths: brand recognition, skilled workforce, innovative technology. Leverage these for advantage.
- Weaknesses: limited resources, outdated processes, communication gaps. Address these to improve efficiency.
Analyzing External Factors:
- Opportunities: emerging markets, changing customer preferences, new partnerships. Seize these to fuel growth.
- Threats: increased competition, regulatory changes, economic downturns. Understand these to mitigate risks.
Benefits for Business Analysts:
- Informed decision-making guides investments, resource allocation, and strategic direction.
- Improvement Focus: Identifies areas for internal strengthening.
- Opportunity Recognition: Paves the way for proactive growth strategies.
- Contingency planning helps prepare for and mitigate potential threats.
Explain the use case, user story, and acceptance criteria.
1. Use Case: Imagine it as a detailed script, outlining how a user interacts with a system to perform a specific action. It describes the steps the user takes, the system’s responses, and the expected outcome, similar to a play for actors and set design.
2. User Story: Think of it as a concise wish list, written from the user’s perspective. It describes what the user wants to achieve and the value they expect from the system, capturing the essence of their desired experience in an easily understandable format.
3. Acceptance Criteria: These are the checkpoints that determine if the user story is truly complete and meets the user’s needs. They define the specific functionalities, performance metrics, and other requirements that must be fulfilled for the story to be considered “done” and ready for user acceptance.
How do you handle managing team conflicts in a project?
1. Clear Communication: Ensure everyone understands project goals, roles, and anticipation to reduce misunderstandings.
2. Active Listening: Listen attentively to all sides of the conflict to uncover the root causes, not just surface disagreements.
3. Open Dialogue: Facilitate respectful discussions where everyone feels heard and encouraged to share their perspectives.
4. Collaborative Solutions: Seek solutions that benefit all team members while aligning with project goals. This might involve compromise, creative problem-solving, or even revisiting project plans.
5. Documentation and Follow-up: Document agreed-upon solutions, timelines, and action items. Monitor progress and be prepared to adapt if needed.
Describe Agile and its importance for a business analyst.
Imagine building a product iteratively, adapting to feedback as you go. That’s Agile in a nutshell! It emphasizes collaboration, short development cycles (sprints), and continuous improvement.
Relevance to Business Analysts:
Faster feedback: Get user feedback early and refine requirements throughout.
Prioritization: Focus on high-value deliverables first, maximizing business impact.
Flexible: Adapt to changing needs and market trends swiftly.
Collaboration: Work closely with developers and stakeholders for better understanding.
Overall, Agile empowers business analysts to deliver valuable solutions rapidly and adapt to a dynamic business landscape.
How can you define priorities with the MoSCoW method?
The MoSCoW method is a powerful tool for defining priorities for requirements. It allows for clear communication, stakeholder alignment, and efficient resource allocation. It follows a two-step process.
1. Understanding the requirements:
Start by thoroughly understanding all the requirements, their purpose, and potential impact. This includes gathering information from various stakeholders through interviews, workshops, and documentation reviews.
2. Categorizing requirements: categorize each requirement based on the Moscow criteria:
a. Must-Haves: These are essential requirements that must be met for the project’s success. They are non-negotiable and typically address core functionalities or business needs.
b. Should-Haves: These are important requirements that add significant value but can be deferred if necessary. They often enhance functionality or user experience.
c. Could-Haves: These are desirable requirements that would be nice to have but can be postponed or even eliminated without compromising the project’s core objectives.
d. won’t-haves: These are requirements that are unnecessary or infeasible for the current project scope or budget. They may be considered for future iterations.
Briefly describe the fishbone diagram (Ishikawa diagram).
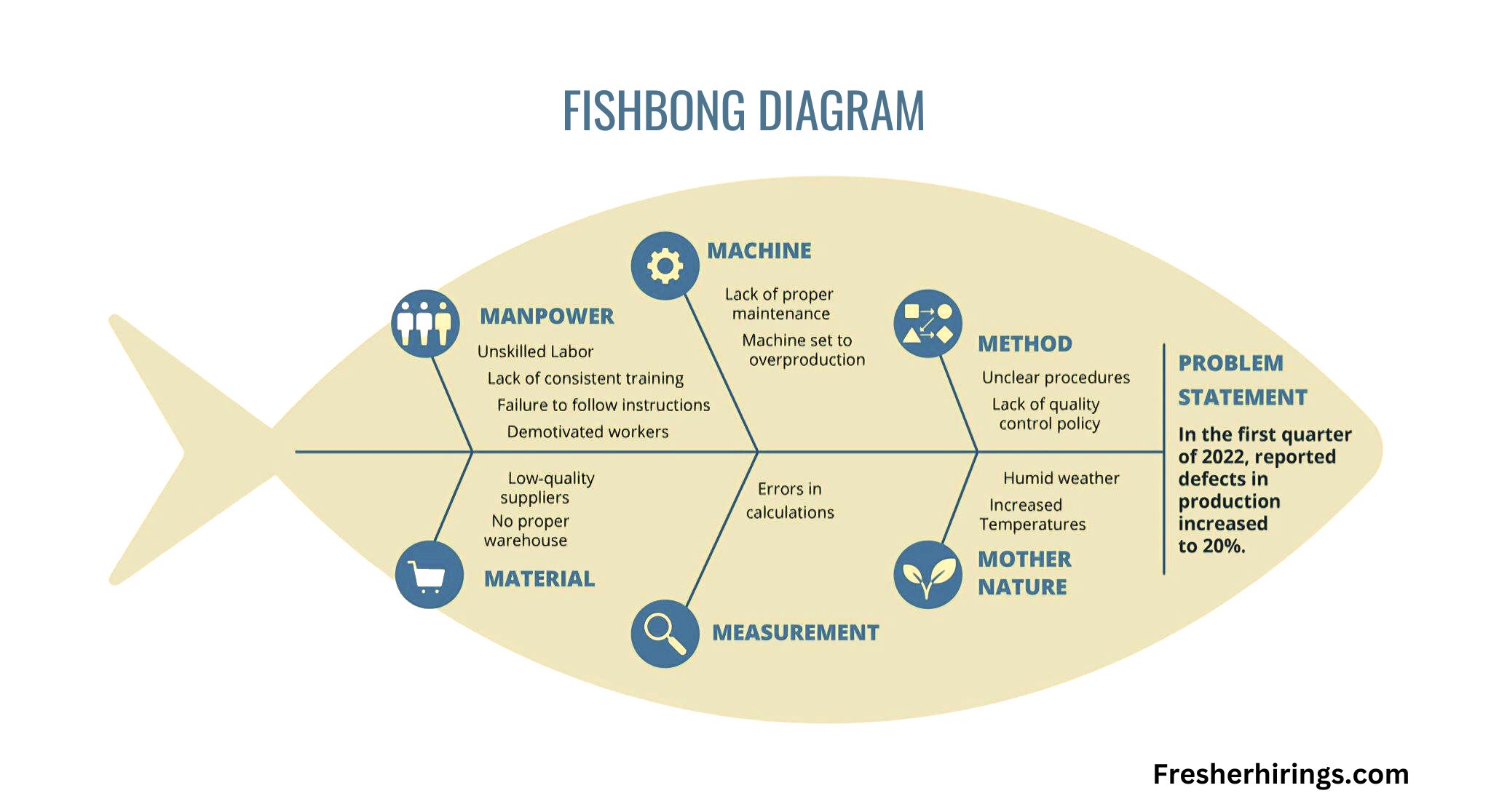
Imagine a fish skeleton: the head points towards the problem, and the bones branching out represent potential causes. Each major branch typically focuses on a specific category of causes, making it a structured brainstorming tool for identifying the root cause(s) of an issue.
How is it used?
Define the problem: Clearly state the issue you’re trying to understand.
Identify main categories: Brainstorm and choose relevant categories for potential causes, like “Materials,” “people,” “Methods,” etc.
Brainstorm causes: Under each category, list possible contributing factors to the problem.
Analyze and prioritize: Evaluate the impact and likelihood of each cause. Drill down and investigate promising branches further.”
Identify root cause(s): Traceback through contributing factors to pinpoint the root cause(s) of the problem.
Benefits:
Visual structure: helps organize information and identify relationships between causes.
Collaboration tool: great for brainstorming and group discussions.
Root cause analysis: Helps move beyond symptoms and find the real source of the problem.
Prioritization: guides resource allocation and solution development.
How can you handle a situation? where a stakeholder requests a feature that is not within the project’s scope or budget?
As a Business Analyst:
Acknowledge: Thank the stakeholder for their suggestion and understand their motivation.
Ask clarifying questions to fully understand the rationale behind the feature request.
a. What problem are they trying to solve?
b. What value do they expect it to bring?
c. Is it a short-term need or a long-term vision?
Explain the state scope/budget constraints and potential project impacts of the request.
Offer options: Explore alternative solutions within the scope or suggest future implementation.
Manage expectations: Be transparent, communicate the decision, and document the request.
Showcase skills: Highlight analytical, communication, and negotiation skills in managing the situation
What are some frequently used tools for a business analyst?
Here are some tools that BAs commonly use:
Requirements Management Tools: Jira, Azure DevOps, Asana, Trello.
Data Analysis & Visualization: Tableau, Microsoft Excel, Power BI, Looker.
Process Modeling & Simulation: Bizagi, Aris, Signavio.
Diagramming & Mind Mapping: Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, Miro, XMind.
Communication & Collaboration: Microsoft Teams, Slack, Confluence.
Surveys & Feedback: SurveyMonkey, Google Forms
In Conclusion: Crack Business Analyst Interview with Deepseek AI. We have uploaded the latest interview question and answers to help you with interview preparation.

2 thoughts on “Crack Business Analysis interview with Deepseek AI”